7 changed files with 53 additions and 38 deletions
Split View
Diff Options
-
+35 -9docs/source/Constant.md
-
+14 -21docs/source/HelloWorld.md
-
+4 -8docs/source/Tensor.md
-
BINdocs/source/_static/contiguous-block-of-memory-ndarray-example-1.png
-
BINdocs/source/_static/contiguous-block-of-memory.png
-
BINdocs/source/_static/tensor-constant-ndarray.png
-
BINdocs/source/_static/tensor-naming.png
+ 35
- 9
docs/source/Constant.md
View File
| @@ -1,6 +1,6 @@ | |||
| # Chapter. Constant | |||
| # Chapter 2. Constant | |||
| In TensorFlow, a constant is a special Tensor that cannot be modified while the graph is running. Like in a linear model $\tilde{y_i}=\boldsymbol{w}x_i+b$, constant $b$ can be represented as a Constant Tensor. Since the constant is a Tensor, it also has all the data characteristics of Tensor, including: | |||
| In TensorFlow, a constant is a special Tensor that cannot be modified while the graph is running. Like in a linear model `y = ax + b`, constant `b` can be represented as a `Constant` Tensor. Since the constant is a Tensor, it also has all the data characteristics of Tensor, including: | |||
| * value: scalar value or constant list matching the data type defined in TensorFlow; | |||
| * dtype: data type; | |||
| @@ -9,9 +9,9 @@ In TensorFlow, a constant is a special Tensor that cannot be modified while the | |||
| ##### How to create a Constant | |||
| ### How to create a Constant | |||
| TensorFlow provides a handy function to create a Constant. In TF.NET, you can use the same function name `tf.constant` to create it. TF.NET takes the same name as python binding to the API. Naming, although this will make developers who are used to C# naming habits feel uncomfortable, but after careful consideration, I decided to give up the C# convention naming method. | |||
| TensorFlow provides a handy function to create a Constant. In TF.NET, you can use the same function name `tf.constant` to create it. TF.NET takes the same name as python binding for the API. Naming, although this will make developers who are used to C# naming convention feel uncomfortable, but after careful consideration, I decided to give up the C# convention naming method. One of reason is for model developer, they don't have to learn a totally new different APIs. | |||
| Initialize a scalar constant: | |||
| @@ -24,19 +24,45 @@ var c4 = tf.constant("Big Tree"); // string | |||
| Initialize a constant through ndarray: | |||
| TF.NET works very well with `NumSharp`'s `NDArray`. You can create a tensor from .NET primitive data type and NDArray as well. An `ndarray` is a (usually fixed-size) multidimensional container of items of the same type and size. The number of dimensions and items in an array is defined by its `shape`, which is a tuple of N non-negative integers that specify the sizes of each dimension. | |||
| ```csharp | |||
| // dtype=int, shape=(2, 3) | |||
| var nd = np.array(new int[][] | |||
| var nd = np.array(new int[,] | |||
| { | |||
| new int[]{3, 1, 1}, | |||
| new int[]{2, 3, 1} | |||
| {1, 2, 3}, | |||
| {4, 5, 6} | |||
| }); | |||
| var tensor = tf.constant(nd); | |||
| ``` | |||
| ##### Dive in Constant | |||
| ### Dive in Constant | |||
| Now let's explore how `constant` works in `eager` mode inside the black box. | |||
| Let's continue using the last examples, we're going to initialize a tensor in an ndarray of `[shape(2, 3), int32]`. | |||
| ##### NDArray | |||
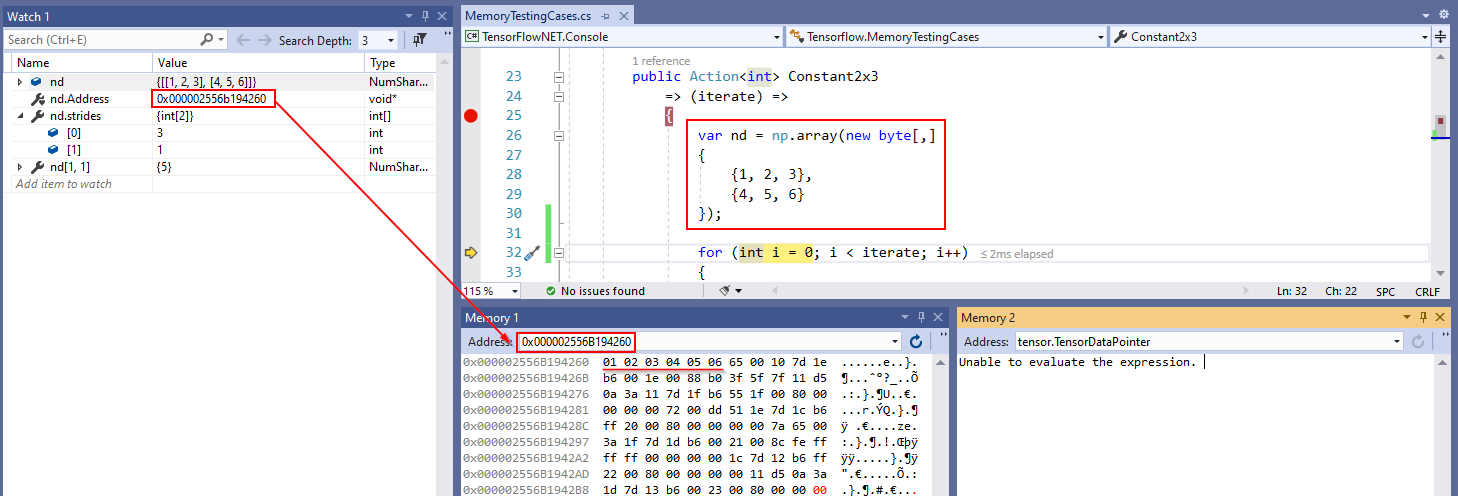
| The first thing we need to know is about `ndarray`'s memory model. The ndarray memory model is a very important data structure, and almost all underlying computation are inseparable from this datb a structure. One fundamental aspect of the ndarray is that an array is seen as a "chunk" of memory starting at some location. The interpretation of this memory depends on the stride information. | |||
| <img src="_static\contiguous-block-of-memory.png" /> | |||
| If we take a look at the real memory allocation in Visual Studio, below diagram helps us understand the data structure more intuitively. The strides keep track the size of every single dimension, help identify the actual offset in heap memory. The formula to calculate offset is: `offset = i * strides[0] + j * strides[1]`. | |||
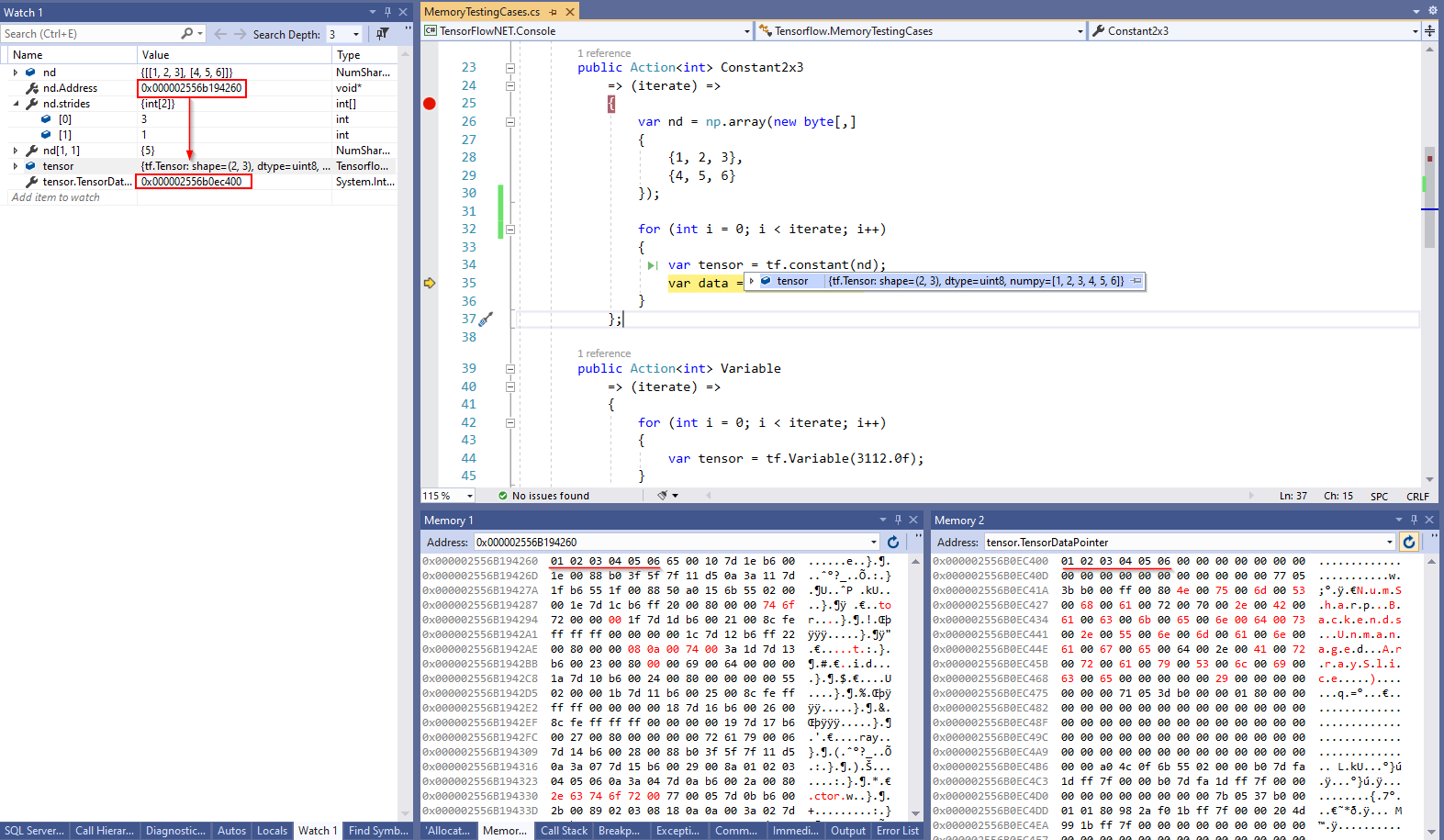
| For example: if you want to seek the value in `[1, 1]`, you just need to calculate `1 * 3 + 1 * 1 = 4`, converted to pointer is `0x000002556B194260 + 4 = 0x000002556B194264` where has a value `05`. | |||
| <img src="_static\contiguous-block-of-memory-ndarray-example-1.png"/> | |||
| Through the above diagram, we know how the data is stored in memory, and then we will look at how the data is transferred to `TensorFlow`. | |||
| ##### Tensor | |||
| If you don't understand very well what `Tensor` is, you can go back to the chapter `Tensor` there is pretty much explanation if you skipped that chapter. Tensor is actually an NDArray that is with more than 2 dimensions. | |||
| TensorFlow will decide whether to copy the data or use the same pointer. Normally speaking, it's more safe whenever you copy data for the following process, especially in interoperating between .NET runtime and C++ runtime that they all have their own garbage collection (GC) mechanism, application will crash if someone access a block of destroyed memory. | |||
| Now let's explore how `constant` works. | |||
| <img src="_static\tensor-constant-ndarray.png" /> | |||
+ 14
- 21
docs/source/HelloWorld.md
View File
| @@ -10,7 +10,7 @@ Let's run a classic HelloWorld program first and see if TensorFlow is running on | |||
| ### Install the TensorFlow.NET SDK | |||
| TensorFlow.NET uses the .NET Standard 2.0 standard, so your new project Target Framework can be .NET Framework or .NET Core. All the examples in this book are using .NET Core 2.2 and Microsoft Visual Studio Community 2017. To start building TensorFlow program you just need to download and install the .NET SDK (Software Development Kit). You have to download the latest .NET Core SDK from offical website: https://dotnet.microsoft.com/download. | |||
| TensorFlow.NET uses the .NET Standard 2.0 standard, so your new project Target Framework can be .NET Framework or .NET Core/ .NET 5. All the examples in this book are using .NET Core 3.1 and Microsoft Visual Studio Community 2019. To start building TensorFlow program you just need to download and install the .NET SDK (Software Development Kit). You have to download the latest .NET Core SDK from offical website: https://dotnet.microsoft.com/download. | |||
| @@ -38,9 +38,9 @@ PM> Install-Package SciSharp.TensorFlow.Redist-Windows-GPU | |||
| ### Start coding Hello World | |||
| After installing the TensorFlow.NET package, you can use the `using Tensorflow` to introduce the TensorFlow library. | |||
| After installing the TensorFlow.NET package, you can use the `using static Tensorflow.Binding` to introduce the TensorFlow .NET library. | |||
| TensorFlow 2.x enabled `Eager Mode` by default. About what eager mode is, I will introduce it in detail in the following chapters. | |||
| ```csharp | |||
| using System; | |||
| @@ -51,33 +51,26 @@ namespace TensorFlowNET.Examples | |||
| /// <summary> | |||
| /// Simple hello world using TensorFlow | |||
| /// </summary> | |||
| public class HelloWorld : IExample | |||
| class Program | |||
| { | |||
| public void Run() | |||
| static void Main(string[] args) | |||
| { | |||
| /* Create a Constant op | |||
| The op is added as a node to the default graph. | |||
| The value returned by the constructor represents the output | |||
| of the Constant op. */ | |||
| var hello = tf.constant("Hello, TensorFlow!"); | |||
| // Start tf session | |||
| using (var sess = tf.Session()) | |||
| { | |||
| // Run the op | |||
| var result = sess.run(hello); | |||
| Console.WriteLine(result); | |||
| } | |||
| Console.WriteLine(hello); | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| ``` | |||
| After CTRL + F5 run, you will get the output. | |||
| ```cmd | |||
| 2019-01-05 10:53:42.145931: I tensorflow/core/platform/cpu_feature_guard.cc:141] Your CPU supports instructions that this TensorFlow binary was not compiled to use: AVX2 | |||
| Hello, TensorFlow! | |||
| Press any key to continue . . . | |||
| 9/20/2020 2:15:09 AM Starting Hello World | |||
| tf.Tensor: shape=(), dtype=string, numpy=Hello, TensorFlow.NET! | |||
| 9/20/2020 2:15:09 AM Completed Hello World | |||
| Example: Hello World in 0.1273463s is OK! | |||
| TensorFlow.NET v0.20.1.0 | |||
| TensorFlow Binary v2.3.0 | |||
| 1 of 21 example(s) are completed. | |||
| Press [Enter] to continue... | |||
| ``` | |||
| This sample code can be found at [here](https://github.com/SciSharp/SciSharp-Stack-Examples/blob/master/src/TensorFlowNET.Examples/HelloWorld.cs). | |||
+ 4
- 8
docs/source/Tensor.md
View File
| @@ -1,4 +1,4 @@ | |||
| # Chapter. Tensor | |||
| # Chapter 1. Tensor | |||
| ### Represents one of the outputs of an Operation | |||
| @@ -8,11 +8,11 @@ | |||
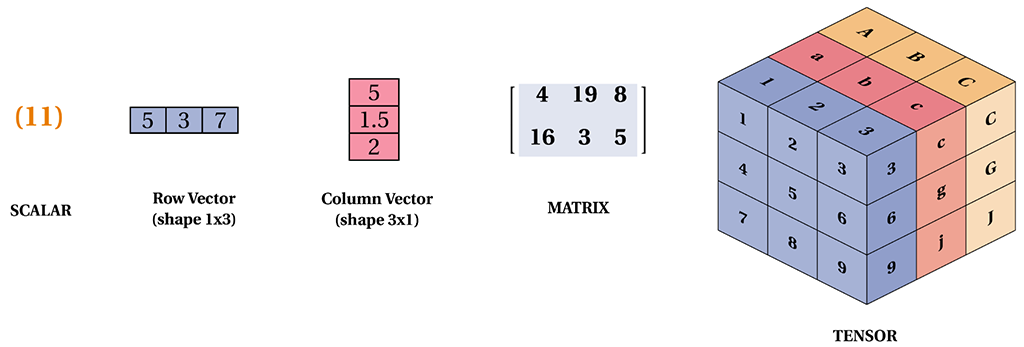
| Tensor holds a multi-dimensional array of elements of a single data type which is very similar with numpy's ndarray. When the dimension is zero, it can be called a scalar. When the dimension is 2, it can be called a matrix. When the dimension is greater than 2, it is usually called a tensor. If you are very familiar with numpy, then understanding Tensor will be quite easy. | |||
| <img src="_static\tensor-naming.png"> | |||
| ##### How to create a Tensor? | |||
| There are many ways to initialize a Tensor object in TF.NET. It can be initialized from a scalar, string, matrix or tensor. | |||
| There are many ways to initialize a Tensor object in TF.NET. It can be initialized from a scalar, string, matrix or tensor. But the best way to create a Tensor is using high level APIs like `tf.constant`, `tf.zeros` and `tf.ones`. We'll talk about constant more in next chapter. | |||
| ```csharp | |||
| // Create a tensor holds a scalar value | |||
| @@ -32,13 +32,9 @@ Console.WriteLine($"t1: {t1}, t2: {t2}, t3: {t3}"); | |||
| ##### Data Structure of Tensor | |||
| TF uses column major order. If we use NumSharp to generate a 2 x 3 matrix, if we access the data from 0 to 5 in order, we won't get a number of 1-6, but we get the order of 1, 4, 2, 5, 3, 6. a set of numbers. | |||
| ```cs | |||
| ```csharp | |||
| // Generate a matrix:[[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]] | |||
| var nd = np.array(1f, 2f, 3f, 4f, 5f, 6f).reshape(2, 3); | |||
| // The index will be 0 2 4 1 3 5, it's column-major order. | |||